Kubernetes is a popular solution for scaling, managing, and automating the deployments of containerized applications in distributed environments. But these highly dynamic and distributed environments require a new approach to monitoring.
More applications now rely on containers and microservices than ever before. According to the 2022 Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) survey, 44% of respondents are already using containers for nearly all applications and business segments, and another 35% say containers are used for at least a few production applications. With apps growing larger and more complex by the day, IT teams will require tools to help manage these deployments.
Since Kubernetes emerged in 2014, it has become a popular solution for scaling, managing, and automating the deployments of containerized applications in distributed environments. Undoubtedly, it will be the orchestration platform of choice for many enterprises as they grow their apps over the coming years.
Although Kubernetes simplifies application development while increasing resource utilization, it is a complex system that presents its own challenges. In particular, achieving observability across all containers controlled by Kubernetes can be laborious for even the most experienced DevOps teams.
But what is Kubernetes exactly? Where does it come from? What problem is it trying to solve, and how does it work? What challenges does it present, and how can you overcome them?
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes (aka K8s) is an open source platform used to run and manage containerized applications and services on clusters of physical or virtual machines across on-premises, public, private, and hybrid clouds. It automates complex tasks during the container’s lifecycle, such as provisioning, deployment, networking, scaling, load balancing, and more. This simplifies orchestration in cloud-native environments.
However, these highly dynamic and distributed environments require a new approach to monitoring Kubernetes infrastructure and applications.
Orchestrating the world: from pipe dream to mainstream
When I started working at Dynatrace in 2011, our customers were using the Dynatrace solution to get deep end-to-end visibility into environments we now refer to as monolithic. The bold organizations were building distributed environments using service-oriented architecture (SOA) and trying to implement enterprise service busses (ESBs) to facilitate application-to-application communication. Although it all looked good on paper, it ended up being difficult to implement.
But a perfect storm was brewing on the horizon. Three revolutions were just beginning and have been feeding on each other since, as commented by John Arundel and Justin Domingus in their 2019 book Cloud Native DevOps with Kubernetes:
- Cloud computing: A revolution in the automation of infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) in an on-demand, pay-as-you-use model
- DevOps and continuous delivery: A revolution in processes, and the way people and software delivery teams work
- Containers and microservices: A revolution in the architecture of distributed systems
Cloud-native refers to cloud-based, containerized, distributed systems, made up of cooperating microservices, dynamically managed by automated infrastructure-as-code.
The change was happening, and it was happening fast; more organizations were adopting containerized deployment methods (such as Docker) and DevOps practices and CI/CD pipelines to confidently deliver business-differentiating features quickly in an increasingly competitive market. At its start in 2013, Docker was mainly used by developers as a sandbox for testing purposes. The challenge at the time was to manage containers at scale in real-world production environments.
What are containers, and why are they so hot?
A container is a unit of software that packages application code and its dependencies together, creating a small, self-contained, and fully functional environment to run a workload (app, service), isolated from the other applications running on the same machine. These packages, known as container images, are immutable, and they are abstracted from the environment on which they run. Their immutability and abstraction make them portable across environments, whether it’s a physical or virtual machine, on-premises, in a data center, or in the public cloud, regardless of the underlying platform or OS. This distributed approach to developing and running apps and services is also known as microservices architecture.
Container runtime engines, such as Docker’s runC, leverage OS-level virtualization capabilities offered from the kernel to create isolated spaces called “containers.” This virtualization makes it possible to efficiently deploy and securely run a container independently of the hosting infrastructure. Because the concern of environmental conflicts is removed, you can run multiple containers on the same node and achieve higher resource utilization, which can reduce infrastructure costs.
But on their own, more than containers is required.
What’s missing here? Well, many things can happen with containers.
As containers are the vehicle of choice for microservices, you wouldn’t expect to run a full-fledged enterprise application in a single container; instead, you would have multiple containers running on different machines to make up a distributed system.
But how will you set up the communication? Who manages the networking aspects? How do you make this system resilient and fault-tolerant? How do you make it scalable?
Containers can’t be used at their full potential on their own. Enter the orchestration platform.
Kubernetes: Container orchestration for the cloud-native era
Think of Kubernetes as a classical orchestra. Replace the composer with a software architect, the conductor with a container platform, the score with a workload, the musicians with containers, the hand gestures with API-based messages, performance with current system state, and vision with the desired system state.
Just like a classical orchestra is a framework for integrating and coordinating all the elements of a beautiful music performance, Kubernetes is a framework for integrating and coordinating all the elements for running dynamic microservices-based applications. Without orchestration, running these applications in production would be impossible.
Kubernetes forged by the rise of Google
If there was any company positioned to understand the problems and limitations of containers before anyone else, it was Google.
Google has been running production workloads in containers longer than any other organization. To operate its infrastructure at high utilization, Google moved its most intensive services into containers. To overcome the challenges of efficiently managing such deployments at a massive scale, they invented a platform to enable container orchestration, known as Borg, which had been Google’s secret weapon for a decade until 2014 when it announced Kubernetes, an open-source project based on the experience and lessons learned from Borg and its successor Omega.
Since then, Kubernetes has taken the container world by storm, becoming the de facto standard for container orchestration, leaving Docker Swarm and Apache Mesos far behind. Google eventually donated the project to the CNCF, while remaining its largest contributor, although companies such as Microsoft, Intel, and Red Hat also contribute and develop their own Kubernetes distributions.
Kubernetes design principles
To understand how Kubernetes works and how to best use it, it’s good to understand the motivations behind its design.
Declarative
Kubernetes manages its resources in a declarative way, which means you specify the desired state, and Kubernetes will continuously reconcile the actual state with the desired state. This frees you from telling it what to do or how to do it (the imperative way), so you can spend time doing other things.
Ephemeral
Kubernetes is designed to deal with failures, which can and will happen: servers can go down, processes run out of memory and crash, the network becomes unreliable, and so on. So instead of assuming the platform will ensure the application resources are always up and running, architects should design them to be fault tolerant and make containers disposable and replaceable.
Immutable
Immutable means unchangeable. In the Kubernetes context, that means if you need to make a change to a container workload, you create a new version (image) of it. Deployments are then executed by provisioning based on validated version-controlled images so they’re more consistent and reliable.
Distributed
Kubernetes architecture is distributed, which means each platform component has a well-defined role and clear mechanism of communication (via API). It is can run on multiple machines, which makes it more resilient and fault-tolerant.
Autoscalable
To adapt quickly in dynamic, cloud-native environments, Kubernetes provides resource autoscaling to respond to changes in demand. Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) adjusts the number of instances or replicas based on observed metrics. Vertical pod autoscaling, an add-on, adjusts the resource requests and limits pod CPU or memory usage as needed.
For clusters that run on a public cloud, cluster autoscaling adjusts the number of nodes in the cluster to help control the cost.
Portable
Kubernetes can run anywhere: in public or private clouds, on-premises, on virtual machines, bare-metal servers, or even mainframes, and is portable across OS distributions.
Immutable infrastructure allows to move your workloads without having to redesign your applications, thus avoiding vendor lock-in.
Self-healing
Because of the ephemeral nature of its containerized workload, Kubernetes provides control mechanisms to repair applications – or even the platform itself – in case of failures. It implements multiple control loops, continuously monitoring the components running on the platform and acting if something is wrong or does not correspond to the desired state. If a container fails, Kubernetes will restart it. If a pod encapsulating a container has a problem, Kubernetes will kill it and spin up a new one. If a node becomes unhealthy, Kubernetes will reschedule the workload to run on a healthy node; if a healthy node is not available, Kubernetes can spin up a new machine using cluster autoscaling.
Resource optimization
Because Kubernetes decouples the application workload from the infrastructure, it can choose the most appropriate server to run your application based on the resource requirements defined in your object manifest file. Its immutable infrastructure enables Kubernetes to move those around freely on the platform infrastructure. This flexibility ensures that the system utilizes resources efficiently and achieves much better results than with manual human intervention.
Kubernetes architecture: A primer
Kubernetes provides a framework to orchestrate containers, for example, to run them securely, create cross-node virtual networks, recreate a container if one fails, manage scaling and load balancing, execute rollouts and rollbacks, and manage secrets, including OAuth tokens, passwords, and SSH keys.
A Kubernetes environment is called a cluster. A Kubernetes cluster is made up of node components, which manage individual containers and their workloads, and control plane components, which manage global functions. A cluster can host multiple nodes.
Node components:
- Image: A container image is a file that encapsulates the application, including its dependencies and configurations
- Node: A virtual or physical worker machine with services to run a pod
- Pods: A group of containers that run the application workload deployed to a single node
- Kubelet: An agent running on each node responsible for communication between the cluster and nodes
With Kubernetes, pods — groups of application containers that share an operating system — run across clusters of services, called nodes, independently of compatibility or location.
Control plane components:
- Kube-scheduler: The default scheduler that selects an optimal node for every pod
- Kubernetes API: The flexible REST API that manages all interactions with Kubernetes
- Kube controller manager: The component that handles all control processes
- Cloud controller manager: The interface with a cloud provider’s API
- Etcd: A fault-tolerant distributed key-value data store that keeps the cluster configuration
The Kube-scheduler schedules the pods, allocating available resources based on the CPU and memory requirements of each node. Web server instances are automatically scaled up or degraded based on demand for the software application, which can be millions of users simultaneously.
What is Kubernetes used for? Kubernetes use cases
The primary advantage of using containers over virtual machines (VMs) for microservices architecture is their small size and performance. They can be spun up and down a lot faster, and have instant access to system resources. This frees up processing power and makes them more portable. Other benefits include shortened software CI/CD cycles, efficient resource utilization, high availability, seamless performance regardless of computing environment, and system self-healing by automatically restarting or replicating containers.
Kubernetes is useful if your organization is experiencing any of the following pain points :
- Slow, siloed development hindering release schedules
- Inability to achieve the scalability required to meet growing customer demand
- Lack of in-house talent specializing in the management of containerized applications
- High costs when optimizing existing infrastructure resources
Kubernetes helps overcome these scaling limitations, coding shortfalls, and development delays. Managed service providers supply the infrastructure and technical expertise to run Kubernetes for your organization. Examples include:
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service
- Red Hat OpenShift
- Google Cloud Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Managed service providers make the benefits of the Kubernetes platform accessible for all shapes and sizes of enterprises struggling to meet a variety of business objectives.
Kubernetes enterprise distributions give organizations the option to host their own Kubernetes infrastructure. Examples include:
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform
- Rancher Kubernetes Engine
- Mirantis Docker Kubernetes Service (formerly Docker EE)
- VMWare Tanzu Kubernetes Grid (formerly Pivotal Container Service–PKS)
- D2iQ Konvoy
Despite the flexibility and portability of containers, it’s important to know that splitting up monolithic applications into small, loosely coupled microservices that span multiple containers and environments makes it a challenge for DevOps teams to maintain visibility into the apps and where they run.
Watch the Perform 2024 session “Accelerate release cycles for Kubernetes applications”
How does Kubernetes enable DevOps?
DevOps teams use agile processes to quickly and efficiently deliver new applications and features, and they typically rely on microservices architecture to accomplish their goals.
For developers, containers align well with the distributed nature of microservices architectures and agile development, which speeds up release cycles from months to days, sometimes hours. Because containers include everything needed to run an application and are abstracted away from the underlying infrastructure, DevOps teams can use them to build, test, and run new applications or features without impacting any other aspects of the application environment.
For operations, Kubernetes and containers make deployment easier by eliminating dependencies on the underlying technology stack, like operating systems and middleware. This independence from the infrastructure makes it easier to manage and automate rolling deployments (blue-green, canary), dynamic scaling, and resource allocation.
The flexibility of Kubernetes also makes it easier to scale applications and make development pipelines more resilient. This enables DevOps teams to tap the benefits of containerization at scale without running into the operational and management challenges that would otherwise drain their productivity and internal resources.
The challenges of Kubernetes at scale: The service mesh question
Organizations with large, mature Kubernetes environments eventually graduate to another problem—whether to use a service mesh. A service mesh controls service-to-service communications for large-scale applications to improve application performance and resiliency. These applications comprising many microservices can experience performance challenges as application traffic grows and requests between the various microservices exponentially increase. When this happens, a service mesh provides an effective solution for routing requests between these microservices and optimizing the flow of data between them.
Service meshes can effectively and securely manage the connections between services so applications can continue to perform at a high level and meet service-level agreements. While orchestration platforms, such as Kubernetes, help developers use containers at scale without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure or advanced container management techniques, service meshes let them focus on adding business value with each new service they build rather than having to worry about “utility code” to ensure secure and resilient communication between services.
Service meshes are best suited for large, mature K8s infrastructures.
Observability challenges with Kubernetes
The CNCF 2020 survey revealed that complexity is one of the top challenges in using and deploying containers. This complexity presents unique observability challenges when running Kubernetes applications and services on highly dynamic distributed systems.
Foremost among these problems is that while Kubernetes orchestrates your containers, it doesn’t offer any insight into the internal state of your applications or issues that might be causing slowdowns or stoppages. That’s why IT teams rely on telemetry data to gain a better understanding of the behavior of their code during runtime. But while collecting logs, metrics, and distributed traces is supported by many protocols like Prometheus and OpenTelemetry, the real value comes from understanding how these constantly changing data points relate to each other. It’s in these hard-to-see relationships that performance issues reveal themselves.
Containerized application instances can come and go rapidly. For example, a pod can be scheduled and then terminated in a matter of milliseconds. They can also have billions of dependencies. It’s true that monitoring agents on nodes can track the state of the cluster and alert DevOps teams when anomalies occur, but what if the issue is with the virtualization infrastructure?
DevOps teams need an automated, full-stack observability solution to stay on top of their Kubernetes orchestration platforms. That’s where Dynatrace comes in.
Monitoring the full Kubernetes stack
The Dynatrace platform—powered by the advanced AI engine, Davis—is the only Kubernetes monitoring system with continuous automation that identifies and prioritizes alerts from applications and infrastructure without changing code, container images, or deployments.
For full mastery of Kubernetes, simply deploy the OneAgent Operator, and Dynatrace can:
- Track the availability, health, and resource utilization of Kubernetes infrastructure
- Get an intuitive view of your workloads and quickly identify unexpected replica counts or excessive pod-level resource limits
- Prioritize anomalies and automatically determine the exact root cause
- Automatically discover and instrument thousands of pods with no manual configuration changes.
With this critical information in one centralized interface, all teams within the software development lifecycle will be able to operate from a single source of truth so they can resolve issues faster and focus on innovations.
While DevOps and SRE teams will be happy to learn about these powerful capabilities, Dynatrace’s value extends far beyond just Kubernetes observability. Dynatrace uses its powerful AI to provide end-to-end visibility into the entire software stack, mapping and analyzing dependencies in near real time to determine both the root cause of any disruption and the impact of slowdowns as they pertain to business KPIs.
Regardless of your cloud platform, container runtime, service-mesh layer, or the number of nodes you’re running, Dynatrace makes monitoring your Kubernetes infrastructure—and everything else in your cloud environment—simple.
Further your Kubernetes knowledge
Kubernetes is a hard, complex implementation, and operations at the enterprise level are not a walk in the park, requiring adequate monitoring and a different approach than with classic stacks.
- Take a deeper dive into Monitoring Kubernetes Infrastructure for day 2 operations
- Learn more about Kubernetes: Challenges for observability platforms
- Ready to learn more about how Dynatrace can make you a Kubernetes monitoring pro:See Mastering Kubernetes with Dynatrace
- See how Dynatrace Expands application and infrastructure observability with operational insights into Kubernetes pods
- Successful Kubernetes Monitoring – Three Pitfalls to Avoid
- How AI Solves the Kubernetes Complexity Conundrum
- Hands-on workshop: Dynatrace with Kubernetes
- Need help getting started? Monitor your Kubernetes clusters with Dynatrace
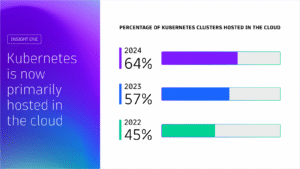
Kubernetes in the wild report 2025
Uncover global Kubernetes adoption trends, cost-optimization strategies, and key tools driving innovation for thousands of organizations worldwide. This report highlights global trends in the technology’s adoption and usage in production environments from thousands of organizations across diverse industries.



Looking for answers?
Start a new discussion or ask for help in our Q&A forum.
Go to forum